INTER-GRANULAR CORROSION
UNIFORM CORROSION
Ferritic and austenitic stainless steels are prone to inter-granular corrosion due to carbide precipitation, a condition known as sensitization to carbide precipitation, caused by improper welding or heat treatment. This phenomena can lead to stress corrosion cracking in marine environments. Means to suppress sensitization, such as during welding, include minimizing holding times at temperatures from 425 ºC to 870 ºC and using proper filler metals with alloying ingredients to prevent carbide precipitation. The sensitized alloy exhibit chromium-rich precipitates at grain boundaries and chromium-depleted zones adjacent to the grain boundaries. These sensitized zones become prone to corrosion attack because of insufficiency of chromium.
The inter-granular corrosion susceptibility and the degree of sensitization (DOS) of stainless steels can be quantified by an electrochemical reactivation test (EPR) or by a double-loop electrochemical potentiokinetic reactivation test (DL-EPR). Duplex stainless steels composed of ferrite and austenite phases exhibit high resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, provided that there is absence of grain boundary precipitates.
Ferrous and non-ferrous metals can also experience inter-granular cracking when exposed to hydrogen from hydrogen sulfide. Metals in contact with hydrogen sulfide environments will react absorbing hydrogen which can build up near grain boundaries promoting stress concentration and eventually lead to inter-granular fracture.
Detecting the susceptibility to inter-granular attack in austenitic stainless steels is done according to ASTM A262. Inter-granular corrosion in wrought nickel-rich chromium-bearing alloys is detected according to ASTM G28.
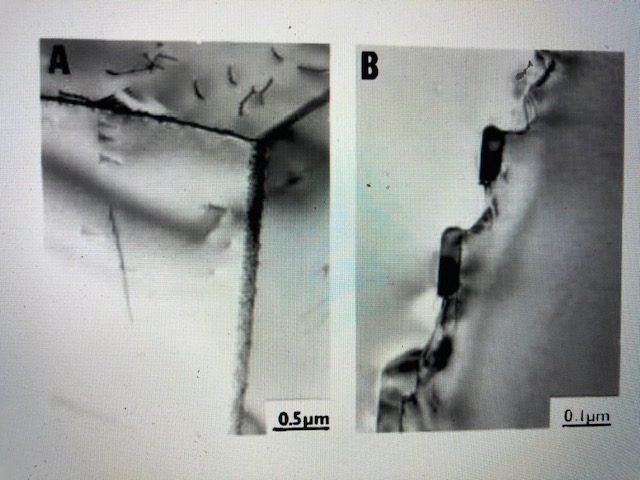
Carbides collecting along the grain boundaries of 304 stainless steel sensitized at 675 ºC for 0.5 hour (A) and for 72 hours (B)*. [*M. G. Lackey, 1980, p. 118; Ph.D Thesis on Inter-granular Stress Corrosion Cracking of Sensitized Austenitic Stainless Steel].
